- Home
- Appendicitis
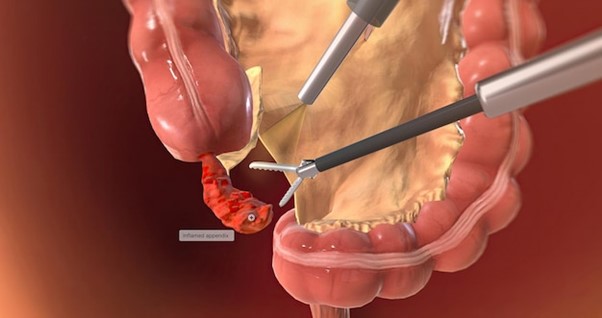
What is Appendicitis?
Appendicitis is an inflammation of the appendix, a small, tube-shaped pouch attached to the large intestine. This condition is considered a medical emergency that typically requires prompt surgical intervention to remove the appendix.
Symptoms of Appendicitis
The most common symptom of appendicitis is a sudden pain that begins around the navel and often shifts to the lower right abdomen. The pain tends to intensify over a period of 12 to 18 hours and can become severe. Other symptoms may include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Fever
- Swelling in the abdomen
- Inability to pass gas
Causes of Appendicitis
The exact cause of appendicitis is often unclear, but it is generally believed to result from a blockage of the appendix, which can be due to:
- Hardened stool
- Foreign bodies
- Infection, which may cause swelling of the appendix
Diagnosis and Treatment
Appendicitis is diagnosed through a combination of physical examinations, laboratory tests, and imaging studies such as an ultrasound or CT scan. The primary treatment for appendicitis is an appendectomy, a surgical procedure to remove the inflamed appendix. This can be performed using:
- Laparoscopic surgery: A minimally invasive technique involving small incisions and the use of a camera.
- Open surgery: A single, larger incision in the abdomen to remove the appendix.
Importance of Prompt Treatment
If left untreated, an inflamed appendix can rupture, leading to a serious condition called peritonitis, an infection of the abdominal cavity. Therefore, recognizing the symptoms and seeking immediate medical attention is crucial for preventing complications and ensuring a quick recovery.

